How to understand the parameters of the lighting industry?
A comfortable and efficient lighting environment can not only enhance the artistic effect of the space, but also increase the sensory experience and bring a better livable environment for people. However, when actually choosing lamps, most people have only a half-knowledge about the lighting parameters, and after buying them in a hurry, they are not satisfactory to use, which is nothing compared to the beauty in their imagination. If you want to see through the secrets behind the parameters at a glance, you urgently need a lighting parameter manual.
With LANGY’s collection and verification, we list here most of the professional parameter descriptions in the lighting industry, hoping to help you when choosing lamps.

LIGHT INTENSITY
The lighting design has light and dark, and choosing the appropriate brightness of the light source can properly set off the atmosphere. Whether the light is on or not, the relevant parameters mainly include the following points;
1.Luminous Flux (LM)
Luminous flux is the total amount of visible light emitted by the light source per unit time, and the unit is lumens (Lm). For example, when we usually say that the light is not bright enough, it refers to the luminous flux.
In general, the higher the power of the same type of lamp, the greater the luminous flux. For example, the luminous flux of a 40W ordinary incandescent lamp is 350-470Lm: while the luminous flux of a 40W ordinary straight tube fluorescent lamp is about 2800Lm, which is 6 to 8 times that of an incandescent lamp, while the luminous flux of a 40W LED lamp is average It can reach 4000-6000lm, which is 10 times that of incandescent lamps and twice that of fluorescent lamps.
2.Luminous Efficacy (LM/W)
Generally speaking, the luminous flux and illuminance need to be measured to know the specific value. When actually purchasing lamps, there is another very important parameter that affects the brightness of the light source – [light effect].
Luminous efficacy (lm/W) is luminous efficiency, which refers to the ability of a lamp to convert electrical energy into light. In other words, how many lumens (lm) of light can a lamp produce per watt. The same power, the higher the luminous efficiency, the greater the luminous flux, and the more energy-saving.
Note: High power ≠ high brightness, because there are differences in light efficiency between different light sources. In terms of luminous efficiency, LED lamps > energy-saving lamps > incandescent lamps.
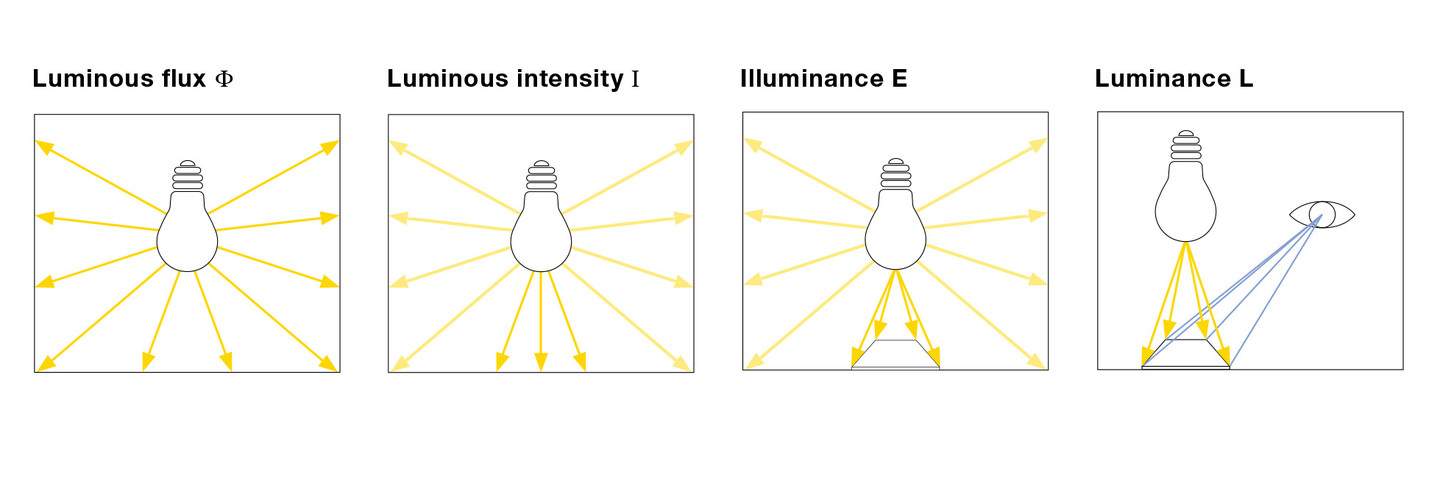
3.Light Intensity (CD)
The luminous flux emitted by a light source within a unit solid angle in a given direction is called the luminous intensity of the light source in that direction, referred to as light intensity (unit is cd (candela)).
1CD=1LM/SR (SR is the steradian unit of solid angle), the luminous intensity directly below the 40W incandescent lamp is about 30cd. And above it, because there is no light emitted in this direction by the blocking king of the lamp holder and the lamp holder, the luminous intensity in this direction is zero.
If an opaque pond porcelain umbrella cover is added, the upward luminous flux is reflected downward by the lampshade except for a small amount of absorption, so the downward luminous flux increases, while the solid angle under the lampshade does not change, so the spatial density of the luminous flux increases , the luminous intensity increased from 30cd to 73cd.
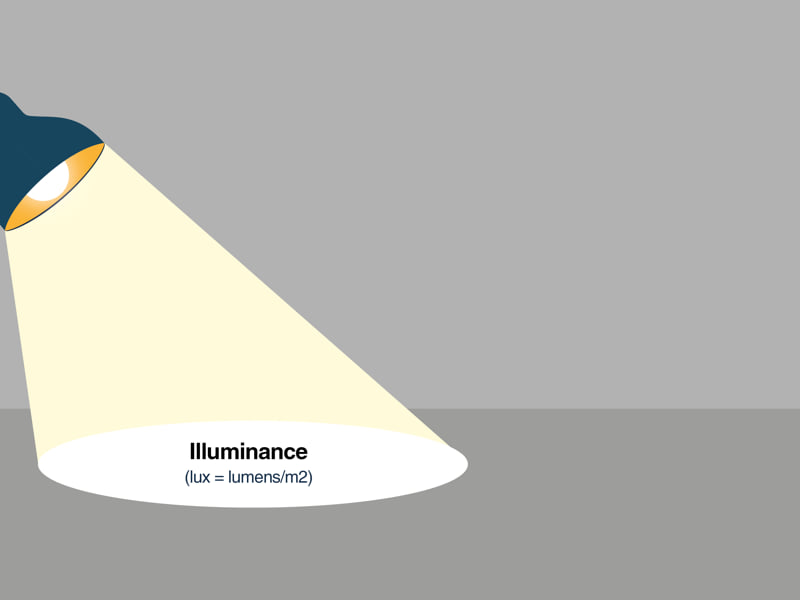
4.Illuminance (LX)
The luminous flux received by the unit illuminated area is called the illuminance (the unit is LX (lux)), that is, 1LX (lux) = 1LM/㎡.
In general, the illuminance is as follows:
- Summer sunshine outdoor: 100000LX;
- Cloudy outdoor: 10000LX;
- Indoor fluorescent lamp: 100LX;
- Desktop 60cm away from 60W desk lamp: 300LX;
- Indoor at dusk: 10LX;
- Night without light source: 0.1LX;
- Candlelight (20cm distance): 10~15LX;
5.Luminance (NT)
The Luminance of a light source in a certain direction (in nt (nit)) is the luminous flux emitted by the light source in a unit projected area and a unit solid angle in that direction.
If each object is regarded as a light source, then the brightness describes the degree of brightness of the light source, and the illuminance just regards each object as an illuminated object. Use a piece of wood to illustrate, when a certain light beam hits the wood, it is called how much illuminance the wood has, and how much light the wood reflects to the human eye is called how much brightness the wood has, that is, the brightness is equal to the illuminance multiplied by the reflectance. In the same position in the same room, the illuminance of a white cloth and a black cloth are the same, but the brightness is different.
LIGHT QUALITY
Whether it can provide comfortable visual enjoyment is the first element in judging the quality of lighting. When choosing lighting, you should not only consider the aesthetics, but also consider safety to create a comfortable and healthy light environment.
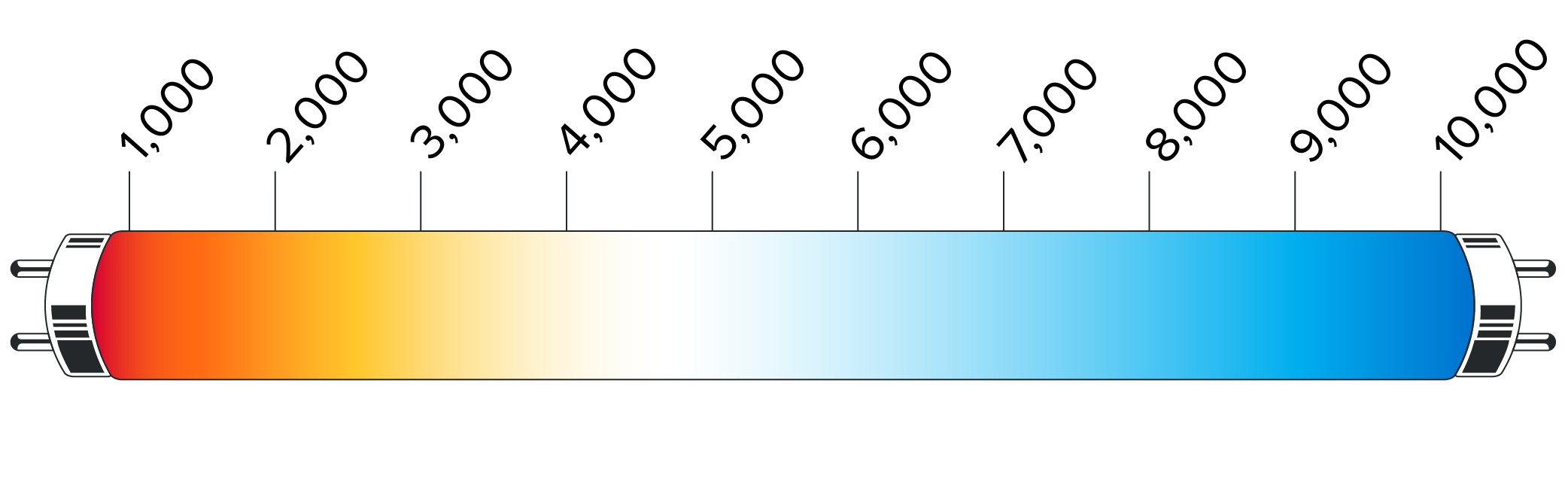
1.Color Temperature (CCT)
Color temperature (CCT) refers to the color of light, and the unit of color temperature is Kelvin (K).
- The color temperature of the red light source is about 800K ~ 900K;
- The yellow and warm color light source is about 3000K;
- The white light source is about 5500K;
- The blue light source is about 8000K ~ 12000K.
The choice of color temperature depends on everyone’s preference.
- Some people like warm colors, so a lamp with a color temperature of about 3000K is suitable for them.
- If you like daylight colors, the color temperature of 5000K ~ 6500K can meet the requirements.
- If you like cool colors, choose LED lighting with a color temperature of 8000K ~ 12000K.
For outdoor lighting, you can choose different color temperatures according to different usage scenarios, which can achieve better lighting effects .
2.Color Rendering Index (CRI)
Color rendering index (CRI) refers to the ability to restore the “true” color of an object, with a score of 100. The larger the value of the color rendering index “Ra”, the closer the object’s color is to the real color.
Generally:
- 80 <RA< 100 is excellent color rendering;
- 50 <RA< 79 is average color rendering;
- RA<50 is poor color rendering.
Choosing lamps with high color rendering index can not only improve the color reproduction of objects, but also bring us a more comfortable lighting environment.
3.Light Decay
Luminous decay refers to the process in which the luminous flux of the light source gradually decays until it fails, that is, the brightness of the lamp gradually decays after a period of use.
Luminous maintenance rate: when the lamp is lit under the specified conditions, the luminous flux measured after the lamp is lit for 100 hours is taken as the initial value, and the ratio of the luminous flux measured after the lamp is lit for 2000 hours is expressed as a percentage (not less than 80%) , as a lighting concept to measure light attenuation.
The popular explanation is that the brightness of the lamp will decrease after being used for a period of time. For different light sources, in the same specified time, the higher the luminous flux maintenance rate, the smaller the light attenuation of the light source.

4.Glare Control
“Glare” will bring discomfort to the human eyes. Living under glare for a long time will affect the health of eyesight. Generally, the requirements for indoor lamps and lanterns will be stricter. Three tips for choosing anti-glare lamps:
- Select the light-emitting mode of the LED surface light source, the light is soft and does not hurt the eyes;
- Pay attention to the lamps with PC lampshades, which can effectively guide the light and make the light output more uniform;
- The light irradiation direction should be as vertical as possible to the horizontal direction of the human eye, such as: up and down light and oblique light strip lights.
The above is the parameter knowledge about lamps that we have carefully sorted out. I hope it can help you. If you have any questions about the above, you can contact us directly. We will provide high-quality solutions according to your specific needs.
